Livestock Farmers are urged to check for Cryptosporidiosis as part of a broader effort to manage livestock health and prevent potential outbreaks, especially in animals such as cattle, sheep, and goats. Cryptosporidiosis, caused by the Cryptosporidium parasite, can infect both humans and animals, leading to gastrointestinal problems, which can have a significant impact on farm productivity and livestock welfare.
These are the reasons Farmers should be concerned:
Livestock Health: Cryptosporidiosis can cause diarrhea, dehydration, and weight loss in infected animals, leading to reduced productivity and higher veterinary costs.
Zoonotic Risk: The parasite can be transmitted from animals to humans, especially through contaminated water or handling infected animals. Farmers and farmworkers are at a higher risk of exposure.
Economic Impact: Affected livestock can suffer from prolonged illness, reducing their growth rates, milk production, and overall performance.
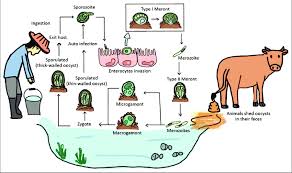
Ways to Check for Cryptosporidiosis:
Monitor Livestock for Symptoms: Look for signs of diarrhea, dehydration, and weight loss in livestock, which are common indicators of cryptosporidiosis.
Laboratory Testing:
Stool Samples: Take samples from affected animals and have them tested at a veterinary laboratory for Cryptosporidium oocysts.
Veterinary Consultation: If symptoms are present, seek advice from a veterinarian who can recommend appropriate tests and treatments.
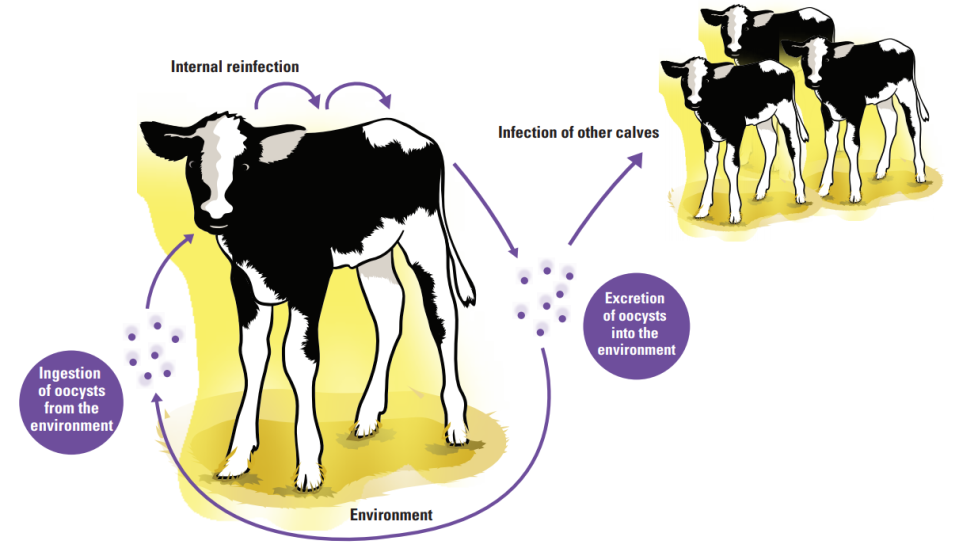
How to Prevent cryptosporidiosis:
Good Hygiene: Farmers should encourage proper hygiene practices, such as handwashing and disinfecting equipment that comes into contact with animals.
Water Quality: Ensure that drinking water sources are clean and free from contamination, as *Cryptosporidium* is often spread through water.
Isolation: Infected animals should be isolated to prevent the spread of the parasite to other livestock.
In Conclusion:
Farmers are encouraged to be vigilant and proactive in detecting and preventing cryptosporidiosis in their herds. Early detection and management can help reduce the economic losses associated with the disease and prevent its spread to humans. It is crucial to stay informed and work closely with veterinarians to keep livestock healthy and productive.